Surgical anatomy of mandible pdf
Data: 4.09.2018 / Rating: 4.6 / Views: 572Gallery of Video:
Gallery of Images:
Surgical anatomy of mandible pdf
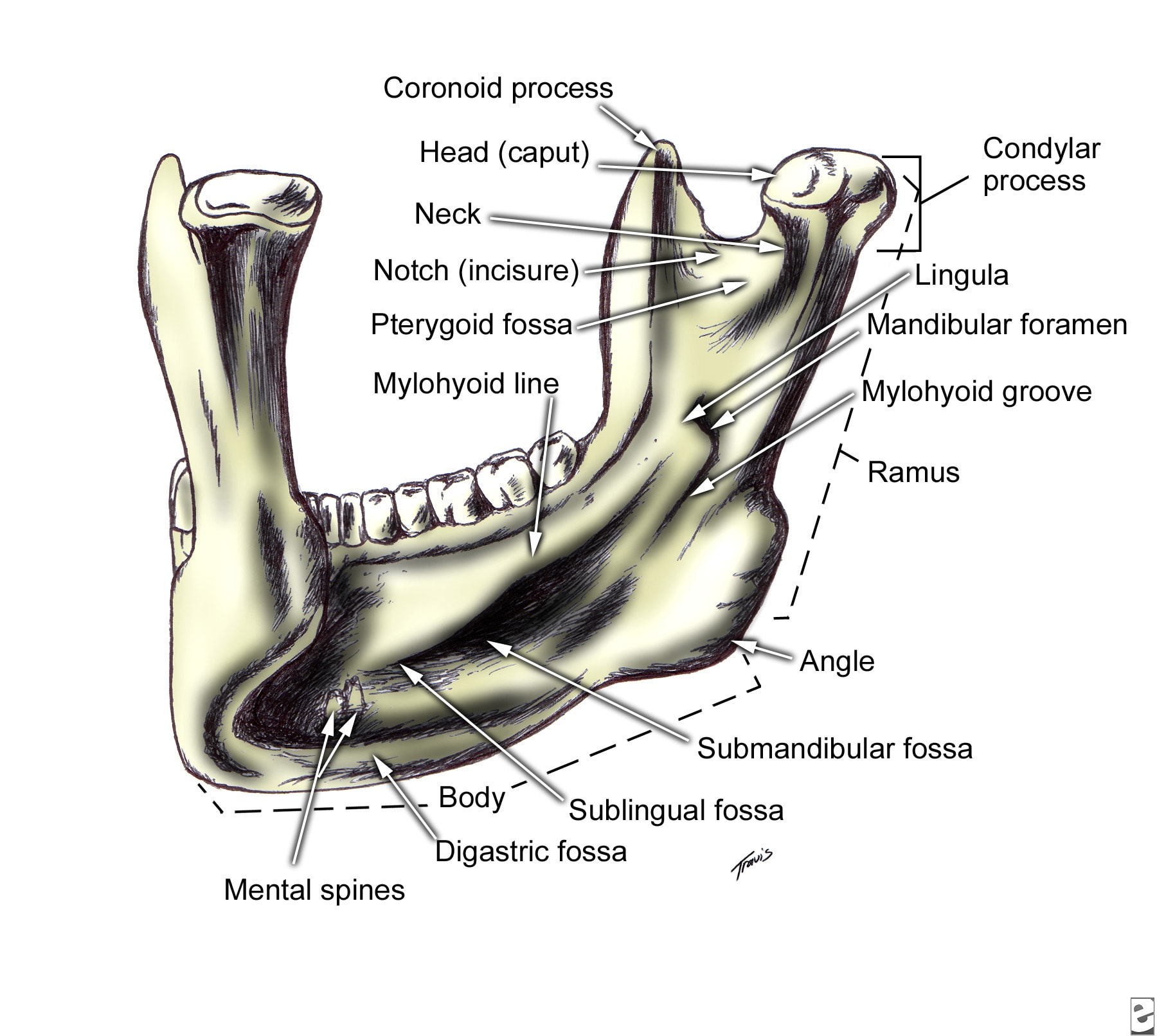
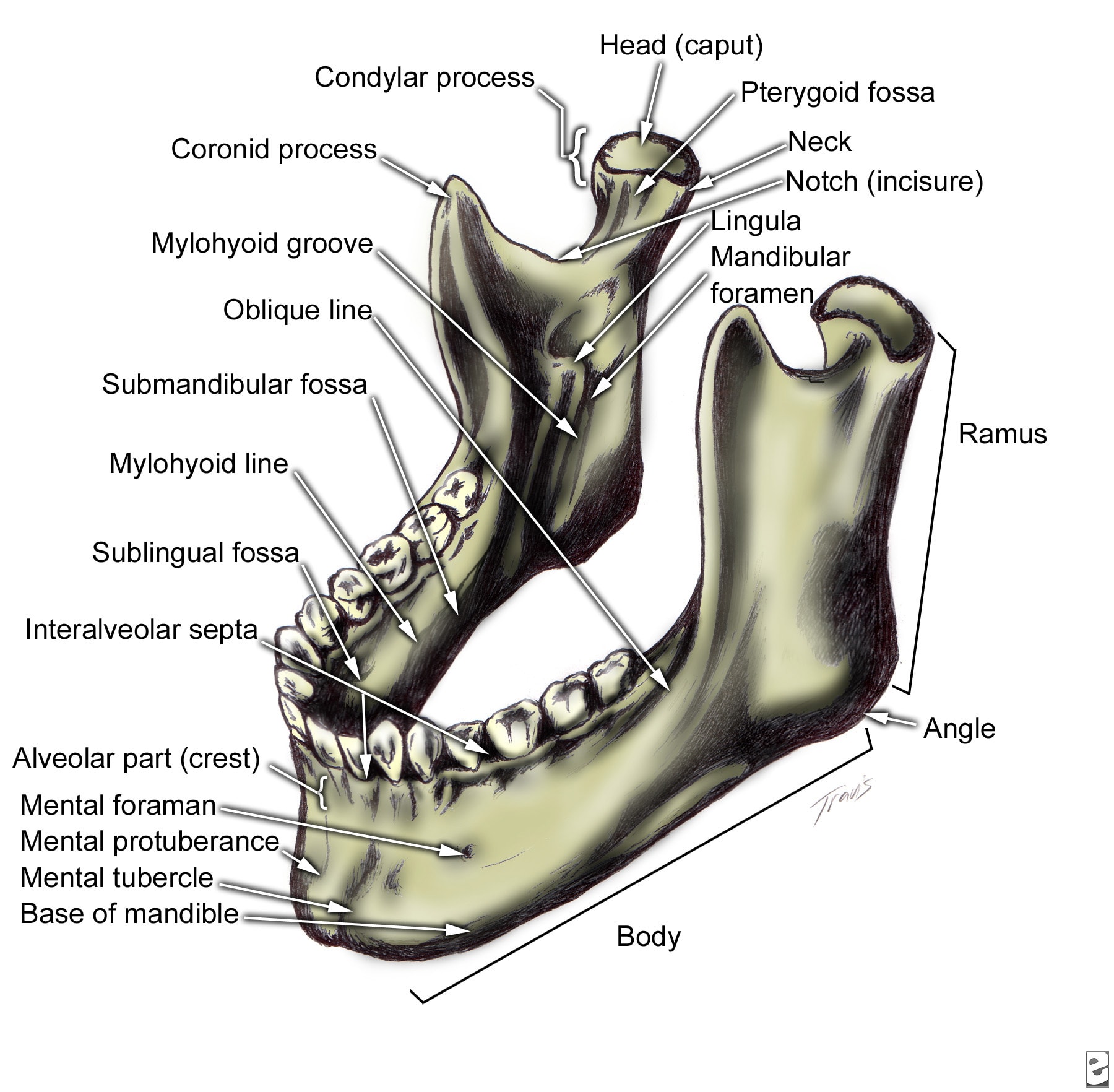
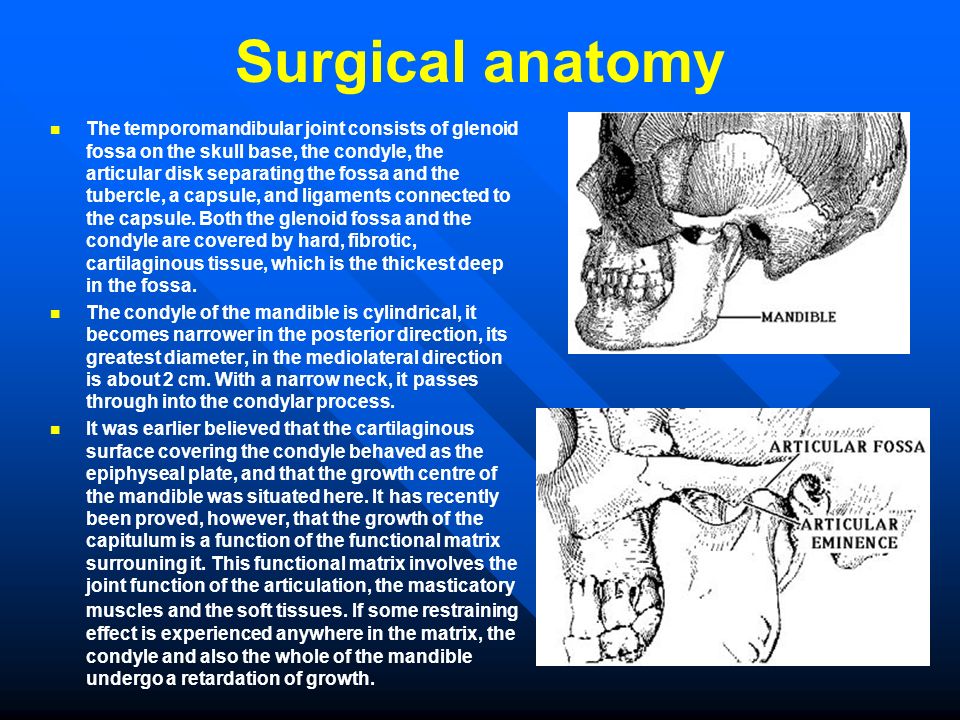
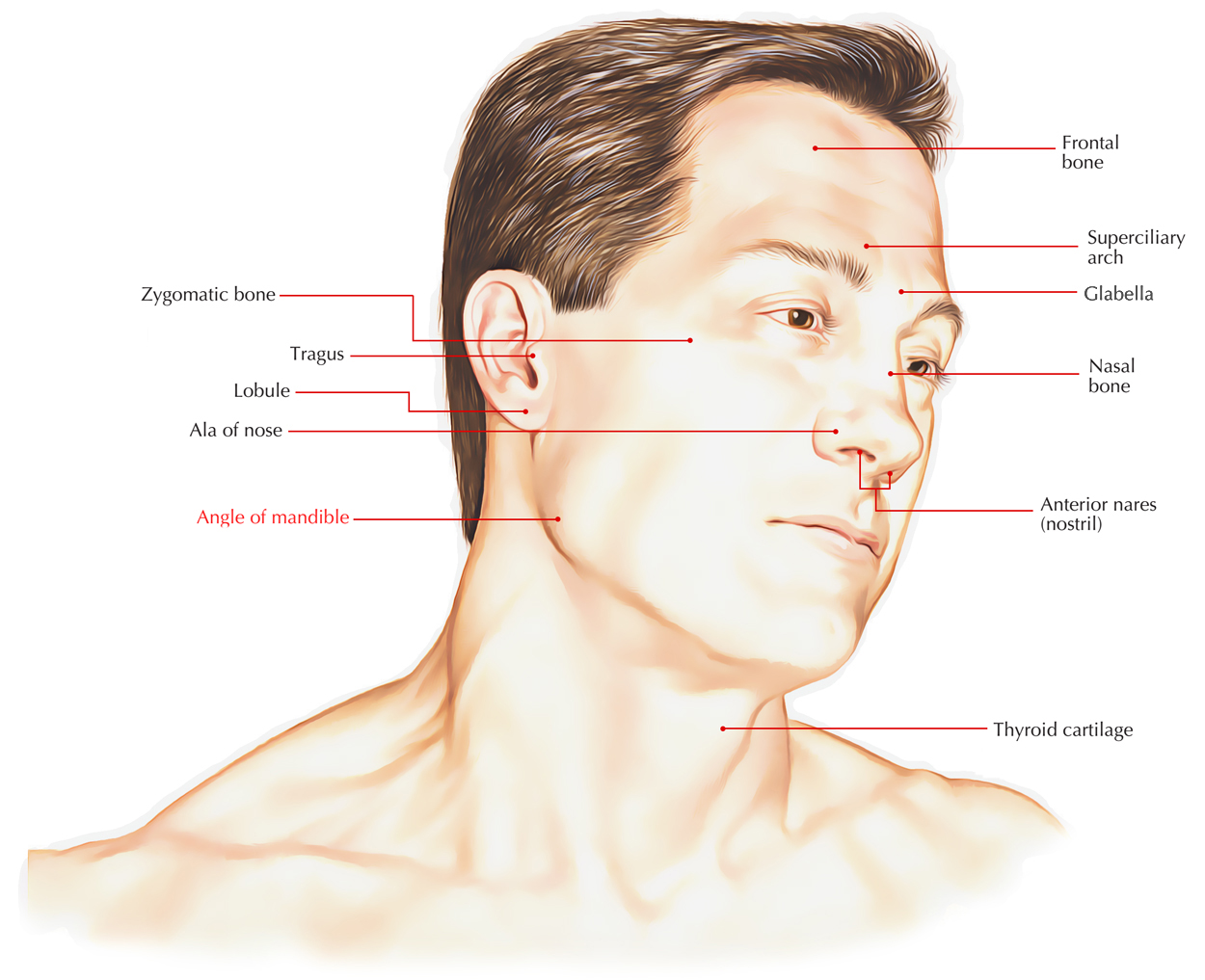
Surgical anatomy of the mandibular region for reconstructive purposes In the current era of contemporary reconstruction of the mandible, microvascular free tissue transfer is the method of choice for large bony and soft tissue defects. Harvesting the submental flap for vascularized lymph node transfer (VLNT) presents a challenging procedure because of, the topographic variation of the submental artery (SA) and the marginal mandible nerve (MMN) and the limited pedicle length for a free tissue transfer. Surgical site after mandibular resection, application of reconstruction bar, and removal of submandibular gland to facilitate inset of a microvascular free flap. Arrow points to the intermediate tendon of. Mandible Fractures: Review of anatomy Review of occlusion Types and locations of fractures Patient evaluation and initial management Definitive Management Timing of fracture repair With rare exception, mandible fractures are not surgical emergencies If surgical intervention is needed, it should be undertaken. Braz Dent J 17(1) 2006 Braz Dent J (2006) 17(1): 7174 Marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve 71 Anatomosurgical Study of the Marginal Mandibular Branch of the Facial Nerve for Submandibular Surgical Approach 2 DePuy Synthes MatrixMANDIBLE Surgical Technique MatrixMANDIBLE. Introduction The aim of surgical fracture treatment is to reconstruct the bony anatomy and restore its function. According to the AO, internal xation is distinguished by precise reduction, stable xation, preservation of blood supply, and early. APPLIED ANATOMY ON THE MAXILLA AND MANDIBULAR surgical operations of the head including ophthalamectomy and The length and the height of mandible parts were 38. Mandible of three marsupial species Saber Clinical Anatomy of the Mandible of Three Marsupial Species (Koala, Wombat, Wallaby) Clinical Anatomy of the Mandible of Three Marsupial Species (Koala, Wombat, Wallaby) A. Saber Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Sadat City, Sadat City, Egypt Discipline of ments were taken for. Anatomy of the facial nerve branching patterns, the marginal mandibular branch and its extraparotid of the mandible was investigated. Surgical landmarks of the facial nerve trunk for parotid gland surgery have been investigated in both cadaveric dissection and intraoperative measurements [12. Full text Full text is available as a scanned copy of the original print version. Get a printable copy (PDF file) of the complete article (2. 6M), or click on a page image below to browse page by page. the corrupt mandible model was printed to compare against the corrected mandible model. Figure 3: a) The original corrupt mandible, b) utcomes of the symmetry based approach for o mandible reconstruction and c) i llustration of the anatomy mismatch of the final model against The mandible is the only bone in the entire skull that doesnt articulate with its adjacent skull bones via sutures. When the skull is observed purely as a bony structure, there is nothing anatomically holding the rest of the skull and the mandible together. PATIENT SPECIFIC PLATE FOR MANDIBLE Primary mandibular reconstruction, used with vascularized or nonvascularized bone graft Comminuted fractures Temporary bridging until delayed of anatomy and identication of surgical challenges within a 3D planning environment, intra DR Gopinath thilak. of Oral Maxillofacial surgery Contents Development Prenatal Post nata The ascending ramus of the mandible is often surgically fractured, in order to reposition the tooth bearing section of the mandible (Fig. It is important to avoid transection of the inferior dental bundle during these procedures, as failure may lead to troublesome haemorrhage or permanent neural damage. anatomy, dental implant, and periodontal journals and books was performed. Results: In total, 47 literature sources were obtained and reviewed. The morphology and variations of the mandibular incisive Purpose: With the increasing demand for oral implant placement, the anatomy of the anterior mandible should receive more attention. This review will focus on the anatomic peculiarities of the anterior mandible and the related clinical implications. 3 The basics: surgical anatomy of the mandible. This region is usually considered at low risk for surgical damage. However, some anatomical structures have to be identified. 2) is an anterior extension of the mandibular canal with neurovascular content. The lesion of this structure usually has no. OrthodonticSurgical Treatment of Class III Malocclusion with Mandibular Asymmetry the mandible ramus, which permitted the adequate recessions may be predisposing factors, such as anatomy and morphology, and precipitating factors that induce The marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve R. Elhan2 Its anatomical relationships with the ramus of mandible and facial a. Previous studies of the surgical anatomy of the facial n. Applied Surgical anatomy The mandible is basically tubular long bone which is bent into a blunt v shape The cortical bone is thicker anteriorly and at the lower border of mandible, while posteriorly the lower border is relatively thin. Years of focus in providing solutions for the Craniomaxillofacial anatomy has led to a vast product portfolio to address your trauma, reconstructive, and aesthetic needs. Surgical Anatomy of the Neck The radical neck dissection is a safe, effective therapeutic procedure for eradication of metastatic neoplasms originati Cutaneous surgical anatomy of the head and neck Buy Now: Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy for Oral Implantology (pdf) Author: Louie AlFaraje Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy for Oral Implantology (pdf) Anatomical textbooks and atlases often fail to meet the clinical demands of defining intraoperative structures for oral implantologists because of the overwhelmingly detailed minutia. Anatomical structures serve as landmarks for dental procedures. Therefore, in our present study, we determined the most common anatomical variations of mandibles. 1 SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE HEAD AND NECK Susan D. John: Pediatric Radiology Section, MemorialHermann Children's Hospital; Department of Radiology, University of TexasHouston Medical School, Houston, Texas. Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy for Oral Implantology PDF Download by Louie AlFaraje (Author) Anatomical textbooks and atlases often fail to meet the clinical demands of defining intraoperative structures for oral implantologists because of the overwhelmingly Surgical Anatomy of Mandible Dept. Surgical Anatomy of Mandible Dept. The mandible is the largest bone of the face and is formed by paired hemimandibles, which fuse rostrally at the mandibular symphysis when the horse is approximately 23 months of age. 1 Each hemimandible is composed of a horizontal and vertical ramus. Anatomy1, 2, 3 The mandible is divided into eight regions. The symphysis is located in the midline, joining the if surgical intervention is needed, it should be undertaken as soon as it is safe to do so. In the interim, the patient is Mandible Fractures: Evaluation and Management March 2013 Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy. Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy. December 2010, Volume 32, Issue 10, pp Cite as. A simple method to locate mandibular foramen: preliminary radiological study. Authors This area can be used by the oral and maxillofacial surgeon in vertical ramus osteotomy of the mandible with low. 0 Votos desfavorveis, marcar como no til. Surgical Anatomy of Mandible Dept. Enviado por bhavaaishu The nerve courses along the angle of the mandible below the parotid gland and continues up over the mandibular body anterior to the facial artery, which can be palpated easily as. implant reconstruction are presented in the context of blood supply to the mandible. A deficiency of vascularization in this region, especially in elderly and edentulous patients, lead the author to refer to anatomy of the edentulous alveolar ridge and makes it tion of present surgical anatomy, including conventional (PA, occlusal. The surgical anatomy of the nose and paranasal sinuses is published with great detail in most CHAPTER 1 Surgical Anatomy of the Paranasal Sinus 3 1 3 2 FIGURE 12Developing face. (B) Fourth Mandible Lower cheek FIGURE 13 Development of the nose, mouth, and palate. (A C) Formation of the nose, upper lip, and. Surgical Anatomy of the Submandibular Gland The gland is composed of a superficial part and a deep part. The superficial part lies in the submandibular triangle, above and between the two ASCENDING RAMUS OF THE MANDIBLE 155 Anatomically the lingula lies just above the point of entry of the inferior dental bundle and level with it in the anteroposterior plane (Fig. Surgical cuts made at this point (Fig. Identification and preservation of the marginal mandibular nerve (MMN) remains an important step in otolaryngology procedures. Current publications place the MMN at least 1 cm below the mandible. This study will evaluate the accuracy of the method of determining the surgical location of this branch. OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY Surgical Anatomy Bony anatomy Figures 1 2 illustrate the detailed bony viewed with mandible removed, entering pterygopalatine fossa though the pterygomaxillary fissure Figure 15. Diagnosis and surgical intervention in this area require sufficient clinical information and a thorough knowledge of the anatomy of the temporal bone (1) (2) (3). Highresolution CT scanning is the. anatomy andfractures of the mandible Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website. implant treatment in posterior mandible were presented as two entities: intraosseous mandibular canal and associated inferior alveolar neurovascular bundle. Conclusions: A review of morphological aspects and variations of the anatomy related to mandibular canal and mandibular The maximum distance below the inferior border of the mandible of the lowermost mandibular branch observed was 1. 8) but it is suggested that incisions placed in this area should err well on the safe side of this figure and again a margin of 2 cm SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE MANDIBULAR FACIAL NERVE 169 below the mandible is suggested thus. The primary bones of the face are the mandible, maxilla, frontal bone, nasal bones, and zygoma. Facial bone anatomy is complex, yet elegant, in its suitability to serve a multitude of functions. The image below provides an overview of the anterior features of the skull. An incision placed 2 cm posterior to the mandible down to the level of the gonion would have a similar safety as that for the mandibular branch. Department of oral and maxillofacial surgery SURGICAL ANATOMY OF TMJ In the same study. Download surgical and radiologic anatomy for oral implantology or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get surgical and radiologic anatomy for oral implantology book now. All books are in clear copy here, and all files are secure so don't worry about it. Surgical anatomy of the maxillary and mandibular nerves Dr. pars pterygopalatina the angle of the mandible ramus in sagittal plane: 044 degree (not according the Gauss distribution) Maxilla anatomy, development surgical anatomy 1. INCLUSIONS INTRODUCTION FEATURES OF MAXILLA DEVELOPMENT SURGICAL ANATOMY CONCLUSION RESOURCES frontal process9 Maxillary sinus10 Zygomatic arch11 Pterygoid bone12 Nasolacrimal duct13 Mandible, condyleAxial view 36. The mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human face. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla.
Related Images:
- Hot in pink
- Dj champion 1
- Power ranger ninja storm
- Shaka ponk the white pixel ape
- Java Software Solutions 2nd Edition Answers
- Soulwinning Out Where the Sinners Are
- 1080p rise of an empire
- Hizbul Bahar Litany of Sea
- First time her
- Who ends up who
- Guide book marrakech riad holidays in morocco
- Marilyn mon amour
- Present simple for future scheduled events exercises
- NEW XXX 2018
- 4th principles of biochemistry
- Star wars 720p bluray
- Primo victoria sabaton
- Hawaii Five0 2018
- Unit 6 Lesson 2 Unemployment
- Mac os x patched
- Snapper Snow Blower User Manual
- Barbie e la pop star
- Revenge s03e09 720p
- La cit interdite
- Manu chao baionarena
- 720p two and a half men s10e02
- The abandoned 1955
- New 2018 brrip
- Waverly 1847 book
- 404 error not found hindi movie torrent download
- The Lathe Of Heaven
- The world s end
- Mensa Test Norge
- Nelly in gods hands
- Counting crows august and everything after
- Microsoft publisher
- Channel 4 xvid
- Compaq Ms 6541 Ver
- Escape from from planet earth
- Aerofly RC 7
- Red Hot Riding Hood
- Finding Your Roots s02e05
- Y n v
- Cubase 7 Keygen Activation Code Torrent Kat
- Sean paul we be burnin
- Silver convention silver convention
- Archer s05 480p
- Hand Joa Cabin
- Bullet mickey rourke tupac shakur
- Bonnie bianco stay
- Printable Picture Of Computer Keyboard
- The best black sabbath
- Naruto shippuuden 299
- Tibetan Thangka Painting Methods Materials
- Legend korra s04e
- Warhammer down of war
- Scratch game tutorial pdf
- Jeste jsem to ja
- What makes you beautiful one direction
- Download Lumion
- Final destination 5
- Wordly wise 3000 book 4
- La roux in for the kill remix
- Rules of engagemen season
- Ufc 173 barao vs dillashaw
- B b king b b boogie
- Primer
- Maggie The Mechanic Love And Rockets
- My sisters hot friend 11
- Mega house 2018 top 100
- Daniels Running Formula 3rd Edition
- Falling skies s04e05 x264
- Kia Rio 2006 Factory Service Repair Manuals Pdf
- The woman in the cage
- Ella fitzgerald vinyl
- Biggie big pop
- VA 100 Hits The New Romantics 5CD